1. General introduction
With the rapid development of Internet of Things technology, technical terms such as NB-IoT, LoRa, and SigFox appear from time to time in our field of vision. For ordinary readers or those who have just contacted the Internet of Things, it may be confused in front of a large number of nouns. The capital theory of this article will give a detailed introduction and comparison of LoRa and LoRaWN.
In general, LoRa only includes link layer protocols and is very suitable for P2P communication between nodes; at the same time, LoRa modules are also cheaper than LoRaWAN;
LoRaWAN also includes a network layer so that information can be sent to any base station that is connected to the cloud platform. Simply connect the correct antenna to its socket and the LoRaWAN module can operate at different frequencies.
2. What is LoRa?
Although LoRa is often misused to describe the entire LPWAN communication system, strictly speaking, LoRa is a proprietary modulation format owned by Semtech. The SX1272 and SX1276 LoRa chips use a modulation technique called chirp spread spectrum (CSS) to form the physical layer (PHY) of the technology stack.
LoRa has two different protocol stacks: LoRaWAN and Symphony Link. Symphony Link is designed for industrial and enterprise users who require advanced features. LoRaWAN is suitable for LoRaWAN-based mobile networks and is growing faster in Europe.
Low-power wide-area networks (LPWANs) are expected to support billions of devices predicted by the Internet of Things, consisting of many components throughout the system. The physical (PHY) layer defines the electrical specifications of the data transmission at the hardware level. The data link layer is responsible for detecting changes in the PHY layer and establishing a protocol for transmitting data.
3. What is LoRaWAN?
LoRaWAN is an open standard that defines the communication protocol for LPWAN technology based on LoRa chips. LoRaWAN defines Media Access Control (MAC) at the data link layer, maintained by the LoRa Alliance. This distinction between LoRa and LoRaWAN is important because other companies such as Link Labs use a proprietary MAC layer on top of the LoRa chip to create a better hybrid design - called Symphony Link in the Link Labs case.
As mentioned above, LoRaWAN is a media access control (MAC) layer protocol designed for large public networks with a single carrier. It is built using Semtech's LoRa modulation scheme, which covers the following aspects:
Building a public network with LoRa
You may already know that LoRaWAN is not suitable for a private network solution, and it is now more suitable for public wide area networks. The root cause is that in LoRaWAN, all channels are tuned to the same frequency, and it is best to have only one network operation in a single area to avoid collision problems.
Since all gateways in the network are bound to the same server, it is the server's job to determine which gateway should respond to the transmission. In a large network, any given transmission is usually received by multiple receivers, then the server notifies one gateway to respond, and the other gateway ignores the transmission. This process helps avoid downlink and uplink collisions because a single gateway is transmitting and overlapping gateways can simply listen for other transmissions.
In addition, a specific channel can be set for a specific use through the LoRa Alliance. Network operators can also limit the number of downlinks in their network from the server side to ensure that low priority endpoints do not "block" the network due to downlink traffic.
Another challenge in the specific application is that LoRaWAN is mainly the data link (MAC) layer (OSI layer 2), and only some elements of the network layer (OSI layer 3). While this provides a great deal of flexibility for applications, it gives application developers a significant amount of work to provide a complete product. This includes packetization, downlink control, multicasting, and more.
How does LoRaWAN work?
At the most basic level, wireless protocols like LoRaWAN are fairly simple. LoRaWAN is a star or star-to-star topology that is generally considered to be better than a mesh network because of its advantages in maintaining battery power and increasing communication range.
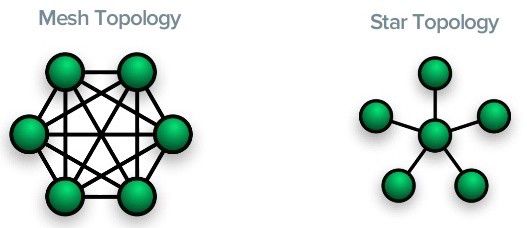
Specifically, the star topology relays messages to the central server through the gateway, and each end node transmits data to multiple gateways. The gateway then forwards the data to the network server, performing redundancy checks, security checks, and message scheduling on the network server.
Two distinct advantages of this design are:
1. Simpler tracking: Since the endpoint sends data to multiple gateways, no gateway-to-gateway communication is required. This simplifies the logic of the end node mobile tracking application.
2. Better public networks: This mismatched relationship allows the central server to resolve collisions, so LoRaWAN may be better suited for deployment on public networks.
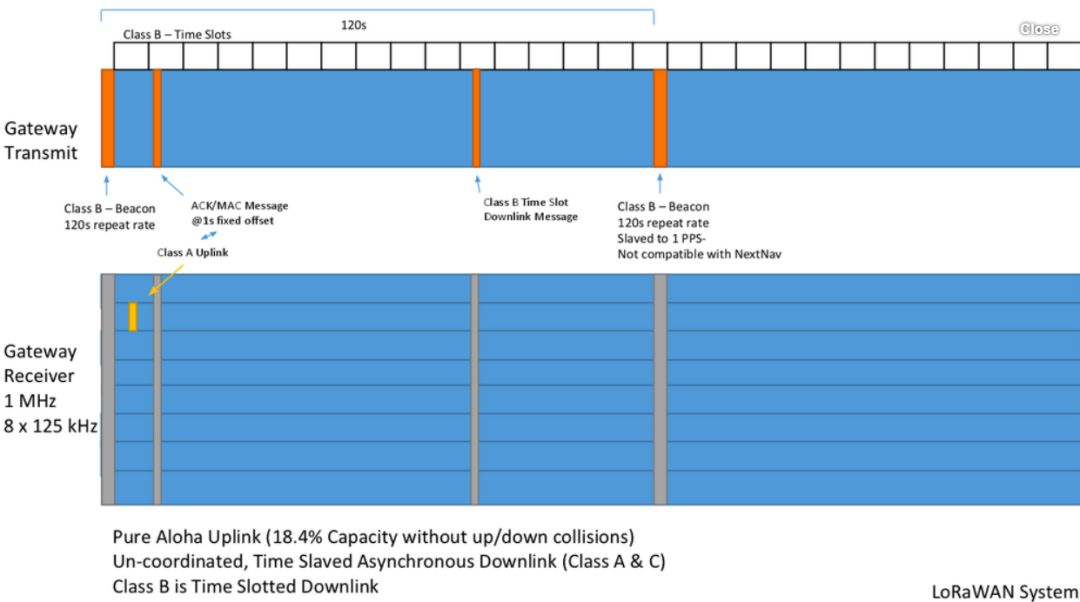
The figure above shows the main operation of LoRaWAN. The top bar shows if the gateway is transmitting. (Orange indicates that it is transmitting; Blue is not transmitting.) The receiver channel is shown at the bottom. Almost all LPWAN systems (including LoRaWAN) have multiple receive channels. Most LoRaWAN systems can receive eight messages simultaneously on any number of frequency channels. .
4.LoRaWAN Class A, B, C
LoRaWAN has three classes that operate simultaneously. Class A is asynchronous, which means that the endpoint does not wait for a specific time to talk to the gateway, but only transmits when needed, and has been dormant until then. As soon as one node completes the transfer, the other node starts immediately. There is no gap in communication. The theoretical maximum capacity of the pure Aloha network is about 18.4% of this maximum. This is mainly due to collisions, because if one node is transmitting and another node wakes up and decides to use the same radio settings to transmit in the same channel, they will collide.
Class B allows messages to be sent to the battery-powered node. Every 128 seconds, the gateway sends a beacon. All LoRaWAN base stations transmit beacon messages at the same time because they are subordinate to one pulse per second (1 PPS). This means that every GPS satellite in orbit will transmit a message at the beginning of each second, allowing time synchronization around the world. All Class B nodes are assigned a time slot within a 128 second period and are told when to listen.
Class C allows nodes to continuously listen and send downstream messages at any time. This is primarily used for AC powered applications because it requires a lot of effort to keep the node up and running at all times.
5. Summary
In summary, in the face of confusing terms like LoRa and LoRaWAN, in fact, as long as the system sorts out, you can find the difference. The following table summarizes the most important features between the two:
| the difference | LoRa | LoRaWAN |
| Nature | LoRa is a modulation technique used in the physical layer of the LoRaWAN network; basically CSS (Chirp Spread Spectrum) modulation for providing different data rates using different spreading factors. | LoRaWAN is used as a WAN (Wide Area Network) wireless network due to its wide coverage capabilities. |
| application | Used as robust modulation in LoRaWAN systems; helps achieve different data rates. | Used as a low power, low data rate and long range wireless system; very popular in IoT / M2M based systems. |
| Location | There are specific functions in the physical layer of the system. | It has four layers: RF, physical layer, MAC and application layer. |
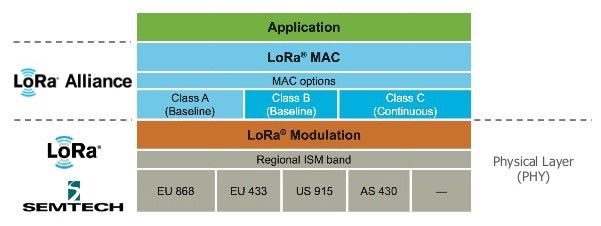
Combine the above diagram, with the simplest formula, you can understand this:
LoRa = PHY Layer
LoRaWAN or Symphony Link = MAC Layer
LoRa + LoRaWAN = LPWAN
Product application:
1 AC air switch
2 AC contactor
3 Mechanical switch and electronic switch
4 Cable and wire
5 Automatic detection and calibration platform
6 Large current capacitor electrical appliances
7 Thermal relay, molded case circuit breaker, small circuit breaker and the required rated current, action current, short-circuit protection current, etc
Technic parameter:
constant current source
Jinan Xinyuhua Energy Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.xyhenergy.com