The development of increasingly intensive computing power has increased the challenges associated with heat. In many systems, the ability of the cooling system places a significant limit on overall performance. Standard cooling components (bulky heat sinks and power-hungry, noisy fans, or quiet but expensive fans) add size constraints to electronic components that are tightly packed. The only way to maximize performance, minimize cooling requirements, and ensure that your electronics work properly is accurate, precise, and comprehensive temperature monitoring throughout your system.
With this in mind, Linear Technology has developed a highly accurate range of temperature monitors that can be easily placed throughout the system. This series includes:
â— The LTC2997 accurately measures its own temperature or the temperature of an external diode.
â— The LTC2996 adds a monitoring function that compares the measured temperature with a high or low temperature threshold and signals the over-temperature alarm to signal any over-temperature conditions.
The LTC2995 integrates the LTC2996 with a dual supply voltage monitor that measures temperature, compares temperature to configurable thresholds, and monitors two supply voltages.
The LTC2997 is a slim, high-accuracy temperature detector
The LTC2997 is available in a 2mm x 3mm 6-pin DFN package and is ideal for measuring the temperature of an FPGA or microprocessor, as shown in Figure 1.
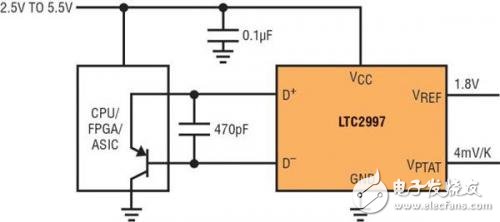
Figure 1: Remote CPU Temperature Detector
To this end, the LTC2997 sends a measurement current to the temperature monitoring diode of the FPGA or microprocessor and produces a voltage proportional to the diode temperature at its VPTAT output. The LTC2997 also provides a 1.8V reference to the VREF output, which can be used as a reference for the built-in ADC in an FPGA or microprocessor. For this configuration using an external detector component, the measurement error is guaranteed to be ±1 °C in the temperature range of 0 °C to 100 °C, and ±1.5 °C in the temperature range of -40 °C to 125 °C. Typical temperature measurement errors will be much smaller, as shown in Figure 2.
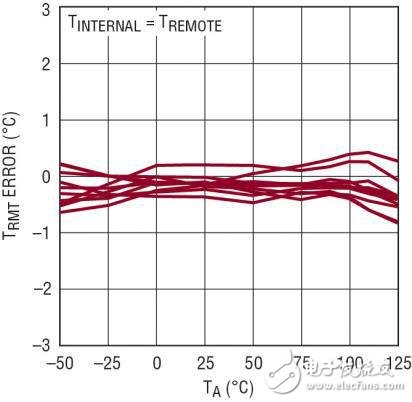
Figure 2: Temperature error as a function of temperature (LTC2997 is at the same temperature as the remote diode)
By connecting the D+ pin to VCC, the LTC2997 can be configured to use its internal temperature detector. The VPTAT voltage has a 4mV/K ramp that is updated every 3.5ms.
Working principleThe LTC2997 measures diode voltage across multiple test currents and uses this measurement to eliminate any process-affected errors and series resistance errors, resulting in impressive accuracy.
T can be solved from the diode equation, where T is the Kelvin temperature, IS is the process influence factor, the magnitude is 10-13A, η is the diode ideality factor, k is the Boltzmann constant, q is Electronic charge:
From this equation, there is a correlation between temperature and voltage, the connection depends on the variable IS affected by the process. The same diode is measured on two different currents (the same IS value), producing an IS-independent expression. The value in the natural logarithm becomes the ratio of the two currents, which is unaffected by the process:
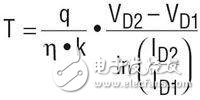
The resistance in series with the remote diode increases the voltage measured at each test current, thus causing a positive temperature error. The composite voltage is equal to:
Where RS is the series resistance.
The LTC2997 removes this error term from the detector signal by subtracting a cancellation voltage (see Figure 3a). The resistor extraction circuit uses an additional measurement current (I3) to determine the series resistance in the measurement path. Once the correct resistance value is determined, VCANCEL is equal to VERROR. Now, since the series resistance and detector temperature can be determined using currents I1 and I2, the temperature-to-voltage converter input signal is immune to errors.
Series resistances up to 1k typically cause temperature errors below 1°C, as shown in Figure 3b, which makes the LTC2997 an ideal device for reading diode detector readings a few meters away from the temperature management system. Indeed, the longest distance is more subject to line capacitance than line resistance. Capacitances greater than 1 nF affect the stability of the detector voltage at various different detection points, thus introducing additional temperature reading errors. For example, a 10 m long CAT 6 cable has a capacitance of approximately 500 pF.
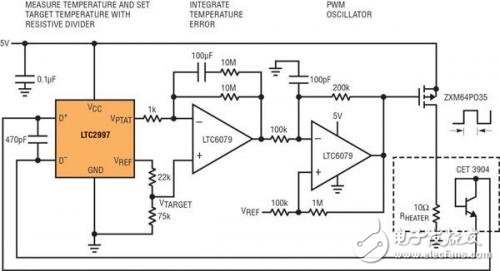
Figure 3: Series resistance cancellation. (a) simplified block diagram; (b) temperature error as a function of series resistance
Unlike many remote diode detectors, the LTC2997 has a reliable temperature measurement algorithm for temperature changes due to its short update time (3.5ms), so it can accurately track rapidly changing temperatures, even during measurement intervals. Figure 4 shows the step response of the internal detector of the device when the LTC2997 is immersed in boiling water immediately after being placed in ice water.
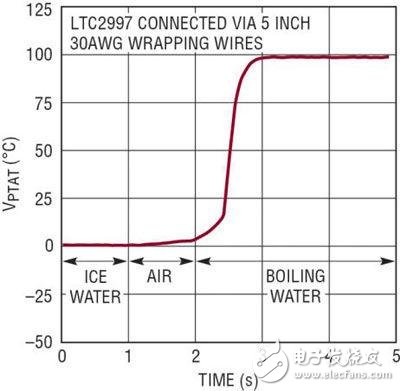
Figure 4: Thermal step response of the LTC2997 internal detector
Idc Connectors,Idc Socket Connector,Idc Electronic Socket Connector,2.00Mm Socket Connector
Dongguan Yangyue Metal Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.yyconnector.com