The intelligent manufacturing system is a human-machine integrated intelligent system composed of intelligent machines and human experts. It can analyze the intelligent activities of human experts in a highly flexible and inefficient way in the manufacturing process. , reasoning, judgment, conceiving, and decision-making, thus replacing or extending part of the mental work of people in the manufacturing environment.
At the same time, the intelligence of human experts is collected, stored, refined, shared, integrated and developed. Features: self-organizing ability; self-discipline; self-learning and self-maintenance; intelligent inheritance throughout the manufacturing environment.

The intelligent manufacturing system architecture is built by three dimensions: life cycle, system level and intelligent function, which mainly solves the modeling research of intelligent manufacturing standard architecture and framework. As shown in Figure 1.
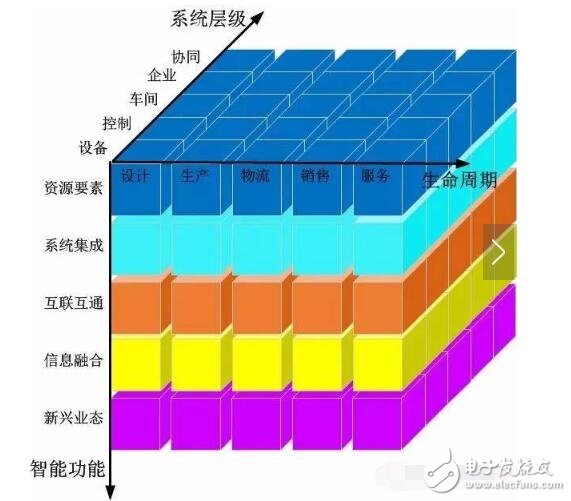
Figure 1 Intelligent Manufacturing System Architecture
1, life cycle
The life cycle is a chained collection of a series of interconnected value creation activities, including design, production, logistics, sales, and services. Activities in the life cycle are interrelated and interact. The life cycle of different industries is not the same.
2, system level
The system hierarchy has five layers from bottom to top, which are device layer, control layer, workshop layer, enterprise layer and collaboration layer. The system hierarchy of intelligent manufacturing reflects the intelligence of the equipment and the Internet Protocol (IP), as well as the flattening trend of the network. Specifically include:
(1) Equipment level includes sensors, instrumentation, bar code, radio frequency identification, machinery, machinery and equipment, etc., which is the material technical basis for the production activities of enterprises;
(2) Control level includes programmable logic controller (PLC), data acquisition and monitoring control system (SCADA), distributed control system (DCS) and fieldbus control system (FCS);
(3) Workshop-level implementation of production management for the plant/plant, including manufacturing execution systems (MES);
(4) Enterprise-level implementation of enterprise-oriented business management, including enterprise resource planning system (ERP), product lifecycle management (PLM), supply chain management system (SCM), and customer relationship management system (CRM);
(5) Collaborative level The collaborative research and development, intelligent production, precision logistics and intelligent services are realized by different enterprises in the industry chain sharing information through the Internet.
3, intelligent function
Intelligent functions include five elements: resource elements, system integration, interconnection, information fusion and emerging formats.
(1) Resource elements include physical entities such as design and construction drawings, product process documents, raw materials, manufacturing equipment, production plants and factories, as well as energy sources such as electricity and gas. In addition, people can also be considered an integral part of the resource.
(2) System integration refers to the integration of raw materials, parts, energy, equipment and other manufacturing resources through information technology such as QR code, radio frequency identification, and software. From small to large, the integration from intelligent equipment to intelligent production units, intelligent production lines, digital workshops, smart factories, and even intelligent manufacturing systems.
(3) Interconnection refers to the interconnection and intercommunication between machines, between machines and control systems, and between enterprises through communication technologies such as wired and wireless.
(4) Information fusion refers to the use of next-generation information technologies such as cloud computing and big data on the basis of system integration and communication to achieve information collaborative sharing under the premise of ensuring information security.
(5) Emerging formats include service-oriented manufacturing models such as personalization, remote operation and industrial cloud.
4, example analysis
The intelligent manufacturing system architecture demonstrates the full picture of smart manufacturing in three dimensions. In order to better understand and understand the system architecture, the programmable logic controller (PLC), industrial robot and industrial Internet are taken as examples to explain the key areas of intelligent manufacturing in the system architecture from three aspects: point, line and surface. Location and related standards.
(1) Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)
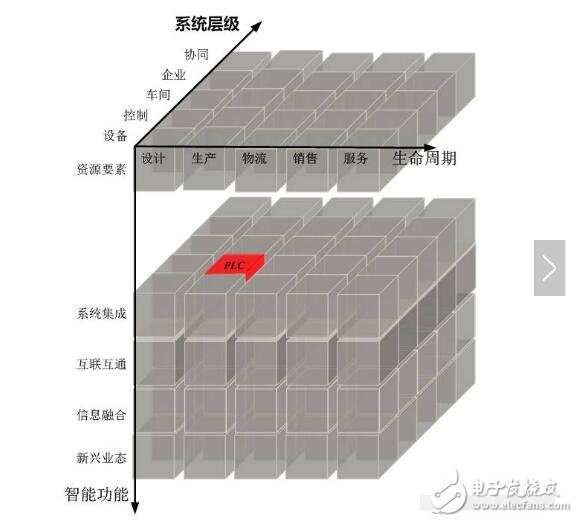
Figure 2 PLC's position in the intelligent manufacturing system architecture
PLC is located in the production process of the intelligent manufacturing system architecture life cycle, the control level of the system level, and the system integration of intelligent functions, as shown in Figure 2. The published PLC standards mainly include:
GB/T 15969.1 Programmable Controller Part 1: General Information Application and Implementation Guide
IEC/TR 61131-9 Programmable controllers - Part 9: Single digital communication interface (SDCI) for small sensors and actuators
(2) Industrial robot
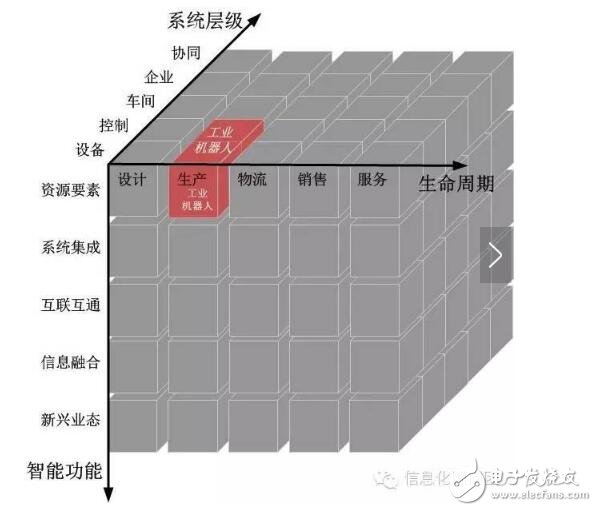
Figure 3 Location of industrial robots in the architecture of intelligent manufacturing systems
Industrial robots are located in the production chain of the intelligent manufacturing system architecture life cycle, the equipment level and control level of the system level, and the resource elements of the intelligent function, as shown in Figure 3. The published standards for industrial robots mainly include:
GB/T 19399-2003 Industrial robot programming and operation graphical user interface
GB/Z 20869-2007 The intermediate code for industrial robots used in robots The industrial robot standards being developed mainly include:
20120878-T-604 Robot Simulation Development Environment Interface
20112051-T-604 Open Robot Controller Communication Interface Specification
(3) Industrial Internet
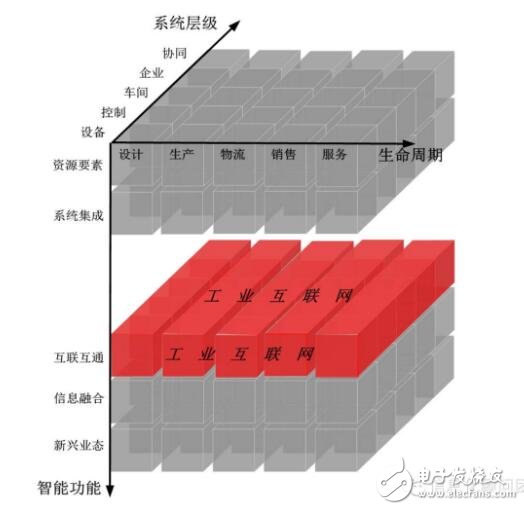
Figure 4 Location of Industrial Internet in Intelligent Manufacturing System Architecture
The Industrial Internet is located at all levels of the lifecycle of an intelligent manufacturing system architecture, at the system level, at the five levels of equipment, control, plant, enterprise, and collaboration, as well as the interoperability of intelligent functions. The published industrial Internet standards mainly include:
GB/T 20171-2006 EPA system structure and communication specifications for industrial measurement and control systems
GB/T 26790.1-2011 Industrial wireless network WIA specification Part 1: WIA system structure and communication specification for process automation
GB/T 25105-2014 Industrial Communication Network Fieldbus Specification Type 10: PROFINET IO Specification
GB/T 19760-2008 CC-Link Control and Communication Network Specification
GB/T 31230-2014 Industrial Ethernet Fieldbus EtherCAT
GB/T 19582-2008 Industrial automation network specification based on Modbus protocol
GB/Z 26157-2010 Measurement and control of digital data communication - Field control systems for industrial control systems 2: ControlNet and EtherNet/IP specifications
GB/T 29910-2013 Industrial Communication Network Fieldbus Specification Type 20: HART Specification GB/T 27960-2011 Ethernet POWERLINK Communication Profile Specification
Characteristics of intelligent manufacturing systemsWhat kind of characteristics does an intelligent manufacturing system have to be called smart manufacturing? There are at least five points: human-computer integration, virtual reality, self-organization and super-melting ability, learning ability and self-maintenance ability, and self-discipline ability. Let's take a look at it. What is self-discipline?
A machine, a device must be self-disciplined, first of all it must be able to perceive, perceive and understand environmental information and its own information, and analyze and judge to plan its own behavior and capabilities. Devices with self-discipline capabilities are called intelligent machines. Intelligent machines show independence, autonomy, personality, and even coordination, operation, and competition with each other. They must have the ability to self-discipline and be able to perceive changes in the environment. Follow the changes in the environment to make decisions to adjust actions. To do this, it must be based on a model of strong support and memory support, and it is possible to have self-discipline.
The intelligent manufacturing system is not just an artificial intelligence system, but an intelligent system integrating man and machine. It not only has logical thinking, image thinking, but also inspiration. It can independently undertake the tasks of analysis, judgment, and decision making. The intelligent system of human-machine integration can better exert the potential of human beings with the cooperation of intelligent machines, so that human-machines can show a relationship of equal cooperation, mutual understanding and mutual cooperation. Therefore, in the intelligent manufacturing system, people with high quality and high intelligence will play a better role. Machine intelligence and human intelligence can be truly integrated, complement each other and complement each other, and always be human-computer integrated.
Recently, China, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, and Guangdong have proposed machine substitutions. Due to labor shortages, difficulties in recruiting workers, and rising labor costs, they have proposed machine substitution. The government has invested a lot of money to subsidize the business. If you implement a machine substitution, the government subsidizes 30%. After doing this, I found that after the introduction of some equipment robots, I will operate, and the quality of the people he wants has completely changed. It turned out to be ordinary laborers. Migrant workers can do it after training. After the robot comes, people are not adapted. People with programming want the robot to serve you, and to maintain the robot, people can't keep up. Therefore, while the equipment is constantly improving, in fact, the working environment and working conditions have changed the requirements of people.
Virtual reality, virtual reality technology is also one of the key technologies to achieve high-level human-computer integration. Virtual reality technology is based on computer, integrating signal processing, animation technology, intelligent reasoning, prediction, anti-true multimedia technology. With a variety of audio and video sensors, virtual displays of the various processes and components in real life can simulate the manufacturing process and future products. From the senses and the visually, it gives people a completely real feeling. It is characterized by changes in people's will and ideas. This new generation of intelligent interfaces combined with human and computer is a distinctive feature of intelligent manufacturing.
We engage in automated factories, logistics automation can also use virtual reality technology, I will design a production line for you, what is the future of this production line, what kind of action is the machine? I can show you through virtual reality through my design, the machine has not come out yet, but I can give you what the whole production line is in the future, what kind of action is the machine equipment, and how the logistics can be carried. Let you see in advance. We are talking about virtual reality to discuss this solution. Which place do you think is not suitable for improvement?
Self-organization and super-melting, in the intelligent manufacturing system, each component unit can form a structure according to the needs of the task. Its capacity is not only manifested in the operation mode, but also in the structural form, so it is called this melting. Sex is called super-melting. It is like a group of human experts who have a biological identity. It can have self-organizing capabilities depending on the environment.
Learning ability and self-recovery ability. The intelligent manufacturing system can continuously enrich the knowledge base in practice and has self-learning ability. During operation, fault diagnosis can be performed, and faults can be eliminated and self-recovery capability can be achieved. This feature is that intelligent manufacturing systems are self-optimizing and adapt to a variety of complex environments. As a smart manufacturing, it should have such characteristics.

The intelligent manufacturing system architecture is built by three dimensions: life cycle, system level and intelligent function, which mainly solves the modeling research of intelligent manufacturing standard architecture and framework.
The life cycle is a chained collection of a series of interconnected value creation activities, including design, production, logistics, sales, and services.
The system level includes equipment layer, control layer, workshop layer, enterprise layer and collaborative layer, which are five layers. The system hierarchy of intelligent manufacturing reflects the intelligence of the equipment and the Internet Protocol (IP), as well as the flattening trend of the network.
Intelligent functions include resource elements, system integration, interconnection, information fusion and emerging business five layers.
(1) Resource elements include physical entities such as design and construction drawings, product process documents, raw materials, manufacturing equipment, production workshops and factories, as well as energy sources such as electricity and gas. In addition, people can also be considered an integral part of the resource.
(2) System integration refers to the integration of various manufacturing resources such as raw materials, parts, energy, equipment, etc. through information technology such as two-dimensional code, radio frequency identification, and software. From small to large, the integration from intelligent equipment to intelligent production units, intelligent production lines, digital workshops, smart factories and even intelligent manufacturing systems.
(3) Interconnection means the interconnection between machines, between machines and control systems, and between enterprises through communication technologies such as wired and wireless.
(4) Information fusion refers to the use of next-generation information technologies such as cloud computing and big data on the basis of system integration and communication to achieve information collaborative sharing under the premise of ensuring information security.
(5) Emerging formats include service-oriented manufacturing models such as personalized customization, remote operation and maintenance, and industrial cloud.

As a mobile multi-purpose platform, tablet computers also provide many possibilities for mobile teaching. The touch-based learning & entertainment teaching platform allows children to efficiently improve their academic performance in a relaxed and pleasant atmosphere. Such tablet computers generally integrate two learning sections of various courses and systematic learning functions. Generally, it includes multi-disciplinary high-quality teaching resources. The education tablet has the following main functions: it has the functions of touch screen input, text editing, picture editing, data storage, data management, wired and wireless Internet access that ordinary tablet computers have; Management functions, search methods support manual search, query by keyword, query by time; text and pictures can be scanned and converted into documents to save.
Education Tablet,learning tablet,leaning machine,New learning tablet
Jingjiang Gisen Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.jsgisentec.com