Currently, mobile wireless technology is transitioning to 4G LTE, and LTE networks in many countries and regions are already commercially available. According to a study by iSuppli, global smart terminal shipments are expected to increase from 246.9 M pcs in 2010 to 506 M pcs in 2014. Major operators have also deployed 3G/4G base station networks in key areas to meet Most of the user's voice and data business needs. However, in some cases, relying solely on base station network coverage, there are still problems.
For example, when a stadium is holding a competition, users need to share the wonderful video on the Internet and need to talk to others. In general, the local 3G/4G base station can better support this voice and data service. However, during the game, a large number of users usually access the local base station network, which requires the local specific base station network to process a large number of voice and data services in a certain period of time, causing the air interface blockage of the base station. The direct result is that the quality of the user's call is degraded, often dropped, the browsing speed of the Internet is greatly reduced, or there is no response for a long time.
In response to this problem, the current industry solution is to combine 802.11n wireless LAN technology and 3G/4G network technology to divert users' data services and voice services. That is, when the intelligent terminal user enters the area covered by the WIFI MIMO network, the data service is turned to the WIFI network, and the cellular network focuses on the voice service, so that the licensed frequency band can have a better call quality, which is the Cellular Offloading solution, as shown in FIG. Shown.
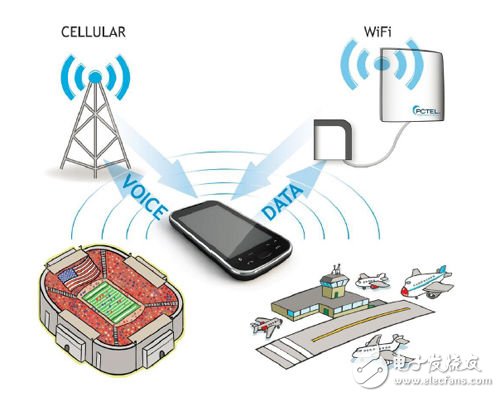
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of the Cellular Offloading scheme.
Cellular Offloading technology requires the same venue to have both 3G/4G network signal coverage and WIFI network signal coverage. Among them, 3G/4G base stations are used for voice communication and WIFI networks are used for data services. A typical WIFI network structure includes: a user client, an antenna, an access point Access Point, a wireless controller AC, and a backbone network. The typical architecture is shown in Figure 2:
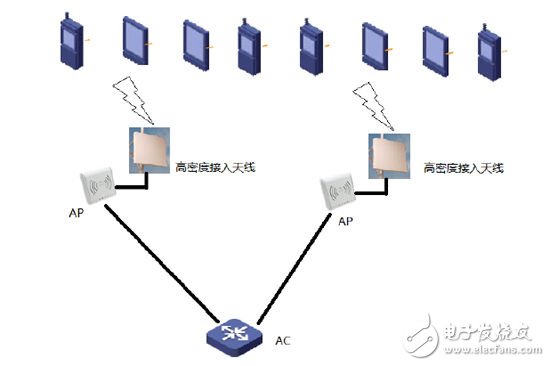
Figure 2: A typical WIFI network structure.
The current WIFI mainstream technology is the 802.11 a/b/g/n protocol, and in practical applications, engineers are most concerned about how to achieve the best coverage and throughput while saving investment. The following article describes how to use the existing technology and products to achieve a good coverage and air interface throughput in high-density applications.
Tinned Copper And PET Braided Sleeve
Tinned copper is used in the sleeve because it offers excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance. The tinning process involves coating the copper strands with a thin layer of tin, which helps prevent oxidation and improves the overall durability of the sleeve.
PET fibers, on the other hand, provide strength and flexibility to the sleeve. PET is a strong synthetic fiber that is resistant to abrasion, chemicals, and UV radiation. It also has good thermal stability, making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
The combination of tinned copper and PET fibers in the Braided Sleeve provides a high level of protection against mechanical damage, electromagnetic interference (EMI), and radio frequency interference (RFI). It also offers good flexibility, allowing for easy installation and routing of wires and cables.
Tinned Copper and PET Braided Sleeve is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and telecommunications. It is used to protect wiring harnesses, cables, and hoses from abrasion, chemicals, and electromagnetic interference.
Overall, Tinned Copper and PET Braided Sleeve is a versatile and reliable solution for protecting and organizing wires and cables in various applications.
Tinned Copper,Pet Braided Sleeve,Tinned Copper Cable,Braided Expandable Sleeving
Dongguan Liansi Electronics Co.,Ltd , https://www.liansisleeve.com