Definition of PLC
A programmable controller is a digital computing operating electronics designed for use in industrial environments. It uses a programmable memory to store operational instructions such as logic operations, sequence control, timing, counting, and arithmetic operations, and controls various types of machinery through digital and analog inputs and outputs. production process. Programmable logic controllers and their associated peripheral devices should all be designed in such a way that they can be easily integrated with industrial control systems and easily expand their functions.
2.PLC classification
A wide range of PLC products have different specifications and performance. For the PLC, the general classification is generally based on the difference in the structure, the difference in functions, and the number of I/O points.
2.1. Classification by Structure
According to the structure of PLC, PLC can be divided into two types: integral type and modular type.
(1) Integral PLC
The integral type PLC integrates the power supply, CPU, and I/O interfaces in a single chassis, as shown in the figure. With a compact structure, small size, low price features. Small PLCs generally use this monolithic structure. The integral PLC consists of a basic unit (also called a host) with different I/O points and an expansion unit. The basic unit has a CPU, an I/O interface, an expansion port connected to the I/O expansion unit, and a programmer or EPROM. The interface to which the router is connected, etc.; the expansion unit has only I/O and power supply, and no CPU. Basic units and expansion units are generally connected by flat cables. Integral PLCs can also be equipped with special function units, such as analog units, position control units, etc., so that their functions can be expanded.
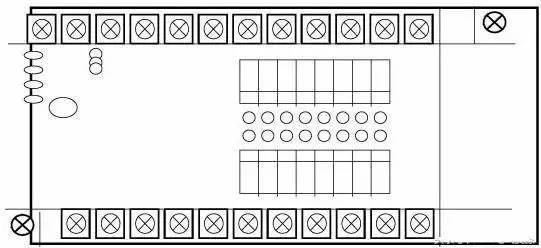
(2) Modular PLC
The modular PLC makes the various components of the PLC into separate modules, such as CPU modules, I/O modules, power modules (some included in the CPU module), and various function modules. The modular PLC consists of a frame or a base plate and various modules that are mounted on the frame or base socket as shown. This modular PLC is characterized by flexible configuration, and can be equipped with systems of different sizes according to needs, and is easy to assemble and easy to expand and maintain. Large and medium-sized PLCs generally adopt a modular structure.
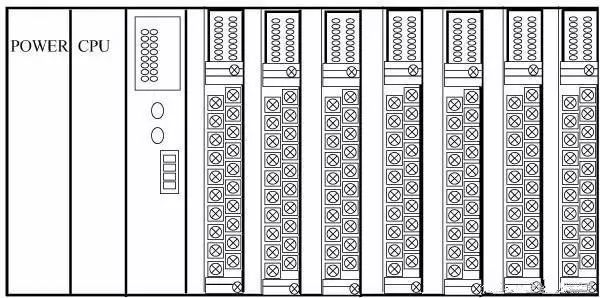
There are also PLCs that combine the integral and modular features to form a so-called stacked PLC. Stacked PLC CPU, power supply, I / O interface, etc. are also separate modules, but they are connected by cables, and each module can be stacked layer by layer. In this way, not only can the system be configured flexibly, but it can also be made compact.
2.2. Classification by function
According to the different functions of the PLC, the PLC can be divided into low-grade, mid-range, high-grade three categories.
(1) Low-grade PLC
The low-grade PLC has basic functions such as logic operation, timing, counting, shifting, self-diagnosis, and monitoring. It can also have a small amount of analog input/output, arithmetic operation, data transmission and comparison and communication functions, etc. It is mainly used for logic control and sequence. Control or a small number of analog control stand-alone control systems.
(2) Mid-range PLC
In addition to the functions of the low-grade PLC, mid-range PLC also has strong analog input/output, arithmetic operations, data transfer and comparison, digital system conversion, remote I/O, subroutines, and communication networking; some can also be added. Interrupt control, PID control and other functions are applicable to complex control systems.
(3) High-grade PLC
In addition to the functions of the mid-range PLC, the high-end PLC also adds arithmetic operations such as signed arithmetic, matrix operations, bit logic operations, square root operations and other special function functions, tabulation, and table transfer functions. The high-grade PLC has stronger communication networking function, which can be used for large-scale process control or constitute a distributed network control system, thereby realizing factory automation.
2.3. Classification by I/O Points
According to the number of PLC I/O points, PLC can be divided into small, medium and large categories.
(1) Small PLC
Small PLCs have less than 256 I/O points, single-CPU and 8-bit or 16-bit processors, and user memory capacity of 4KB or less. For example: Mitsubishi FX0S series.
(2) Medium PLC
Medium-sized PLCs have I/O points between 256 and 2048. They have dual CPUs and have a user memory capacity of 2 to 8 KB.
(3) Large PLC
Large PLCs have more than 2048 I/O points, multiple CPUs, 16-bit or 32-bit processors, and user memory capacity of 8 to 16 KB.
In the world, PLC products can be divided into three major schools geographically. One school is American products, one school is European products, and one school is Japanese products. The U.S. and European PLC technologies are independently researched and developed under isolation from each other, so the U.S. and European PLC products have significant differences. While Japan's PLC technology is introduced by the United States, it has a certain degree of inheritance for the United States PLC products, but Japan's main push product is positioned on a small PLC. The United States and Europe are known for large and medium-sized PLCs, while Japan is known for small PLCs.
The common PLC is shown in the table.
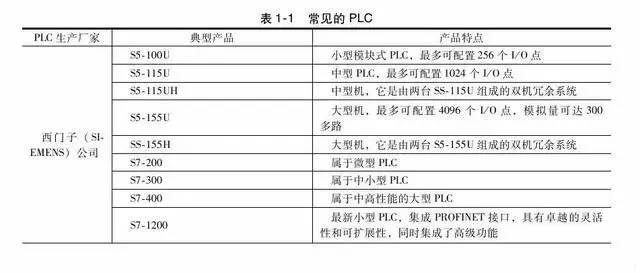
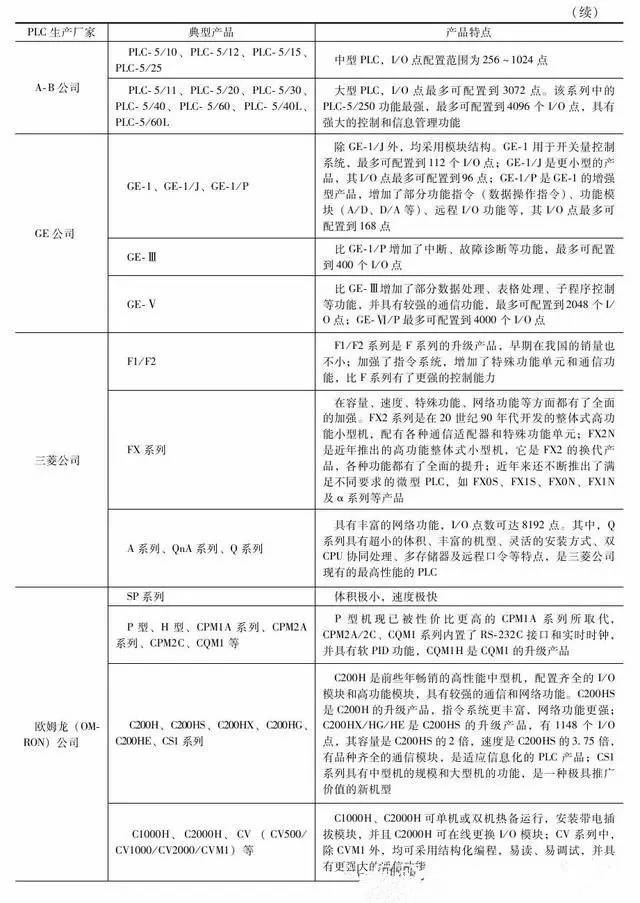
Second, the function and application of PLC
The PLC is designed, manufactured, and developed with the advantages of integrated relay contactor control and the flexibility and convenience of the computer, which makes the PLC have features that many other controllers cannot match.
1. The function of PLC
PLC is a universal industrial automatic control device that is based on a microprocessor and integrates computer technology, automatic control technology and communication technology. It has high reliability, small size, strong functions, simple program design, flexible universal and Convenient to maintain and a series of advantages, it has a wide range of applications in the fields of metallurgy, energy, chemicals, transportation, electricity, etc., and become one of the three pillars of modern industrial control (PLC, robots and CAD/CAM). According to the characteristics of PLC, its function form can be summarized as the following types.
(1) Switch quantity logic control
PLC has a powerful logic computing capabilities, can achieve a variety of simple and complex logic control. This is the most basic and widest application area of ​​the PLC. It replaces the traditional relay contactor control.
(2) Analog Control
PLC is equipped with A/D and D/A conversion modules. The A/D module can convert the analog, such as temperature, pressure, flow rate, and speed, into a digital quantity, and then it is processed by the microprocessor in the PLC (the microprocessor can only process the digital quantity). Control; or after the D / A module conversion into analog, and then control the controlled object, so that the PLC can control the analog quantity.
(3) Process Control
Modern large and medium-sized PLCs are generally equipped with a PID control module that can perform closed-loop process control. When a certain variable in the control process deviates, the PLC can calculate the correct output according to the PID algorithm, and then control and adjust the production process and keep the variable at the setting value. At present, many small PLCs also have PID control functions.
(4) Timing and counting control
PLC has a strong timing and counting function, it can provide users with tens or even hundreds, thousands of timers and counters. The time and count value of the timer can be arbitrarily set by the user during the programming of the user program, and can also be set by the operator at the industrial site through the programmer, thereby realizing the control of timing and counting. If the user needs to count the higher frequency signals, the high speed counting module can be selected.
(5) Sequence Control
In industrial control, PLC step instruction programming or shift register programming can be used to achieve sequence control.
(6) Data Processing
Modern PLC can not only perform arithmetic operations, data transfer, sorting and table look-up operations, but also data comparison, data conversion, data communication, data display and printing, etc. It has strong data processing capabilities.
(7) Communication and networking
Most modern PLCs use communication and network technologies and have RS-232 or RS-485 interfaces for remote I/O control. Multiple PLCs can be networked and communicate with each other. Programs and data exchanges can be implemented between external devices and signal processing units of one or more programmable controllers, such as program transfer, data file transfer, monitoring, and diagnostics. The communication interface or communication processor completes the program and data transfer according to a standard hardware interface or a proprietary communication protocol.
2. Application of PLC
At present, PLC has been widely used at home and abroad in steel, petroleum, chemical, electric power, building materials, machinery manufacturing, automotive, textile, transportation, environmental protection, and cultural and entertainment industries. Usage can be roughly classified into the following categories.
(1) Logical control of the switch amount
This is the most basic and most extensive application field of PLC. It replaces the traditional relay circuit and realizes logic control and sequence control. It can be used not only for the control of single equipment, but also for multi-machine group control and automation lines, such as injection molding machines. , printing presses, staple machines, modular machine tools, grinding machines, packaging production lines and plating lines.
(2) Analog Control
In the industrial production process, there are many continuously changing quantities, such as temperature, pressure, flow rate, liquid level, and speed, all of which are analog quantities. In order for the PLC to process analog quantities, A/D conversion and D/A conversion between analog and digital quantities must be implemented. PLC manufacturers all produce matching A/D and D/A conversion modules, making PLCs for analog control.
(3) Motion Control
PLC can be used for the control of circular motion or linear motion. From the point of view of control mechanism configuration, the direct use of switch I/O modules in the early stage to connect position sensors and actuators now generally use dedicated motion control modules to drive single-axis or multi-axis position control modules for stepper motors or servo motors. . The products of major PLC manufacturers in the world almost all have motion control functions and are widely used in various machinery, machine tools, robots, elevators and other occasions.
(4) Process Control
Process control refers to closed-loop control of temperature, pressure, flow, and other analog quantities. It has a wide range of applications in metallurgical, chemical, heat treatment, boiler control, and other occasions. As an industrial control computer, PLC can compile various control algorithm programs to complete closed-loop control. PID regulation is a method commonly used in general closed-loop control systems. Large and medium-sized PLCs have PID modules. Many small PLCs now have this function module. PID processing is generally a dedicated PID subroutine.
(5) Data processing
Modern PLC has mathematical operations (including matrix operations, function operations, and logic operations), data transfer, data conversion, sequencing, table lookup, and bit manipulation. It can complete data collection, analysis, and processing. These data can be compared with reference values ​​stored in memory to complete certain control operations; they can also be transmitted to other smart devices using communication functions, or they can be printed and tabulated. Data processing is generally used for large-scale control systems, such as unmanned flexible manufacturing systems; it can also be used for process control systems, such as large-scale control systems in the papermaking, metallurgy, and food industries.
(6) Communication and Networking
PLC communication includes communication between PLCs and communication between PLC and other smart devices. With the development of computer control, the factory automation network has developed rapidly. Each PLC manufacturer pays great attention to the PLC's communication function and has launched its own network systems. Newly produced PLCs all have communication interfaces and communication is very convenient. Have launched their own network systems. Newly produced PLCs all have communication interfaces and communication is very convenient.
Third, the basic structure and working principle of PLC
As an industrially controlled computer, PLC and ordinary computers have similar structures; however, there are some differences in the structure due to different occasions and purposes.
1.PLC hardware composition
The basic block diagram of the PLC hardware system is shown in the figure.
In the figure, the host of the PLC consists of a CPU, memory (EPROM, RAM), input/output unit, peripheral I/O interface, communication interface, and power supply. For integral PLCs, these components are all in the same enclosure. For modular PLCs, each component is individually packaged and called a module. Each module is connected through a rack and cable. Each part of the host computer is connected through the power bus, control bus, address bus, and data bus, according to the actual control of the needs of the target with a certain number of external devices, constitute a different PLC control system. Commonly used external devices include programmers, printers, EPROM writers, and so on. The PLC can configure the communication module to communicate with the host computer and other PLCs to form a PLC distributed control system.
The following describes the various components of the PLC and their functions, so that users can further understand the PLC control principle and work process.
(1) CPU
The CPU is the control hub of the PLC. The PLC coordinates work in an orderly manner under the control of the CPU, thereby realizing the control of various devices on the site. The CPU consists of a microprocessor and a controller. It can implement logical operations and mathematical operations and coordinate the work of various parts of the control system.
The role of the controller is to control the entire microprocessor's various components to work in an orderly manner. Its basic function is to read instructions and execute instructions from the memory.
(2) memory
The PLC is equipped with two kinds of memory, namely system memory and user memory. The system memory is used to store the hypervisor. Users cannot access and modify the contents of this memory. User memory is used to store the programmed application and work data status. The user memory section storing the status of the working data is also referred to as a data storage area, which includes an input/output data map area, a timer/counter preset number and a data area of ​​the current value, and a buffer storing intermediate results.
The PLC memory mainly includes the following types.
(1) Read-only memory
(2) programmable read-only memory
(3) Erasable programmable read-only memory
(4) Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory
(5) Random Access Memory
(3) Input/Output (I/O) module
1 digital input module
The switch input device is a variety of switches, buttons, sensors, etc. The PLC input type can usually be DC, AC and AC and DC. The input circuit power can be supplied externally, and some can also be provided internally by the PLC.
2 switch output module
The function of the output module is to convert the control signal of the TTL level output by the CPU to execute the user program into a signal required by the production site to drive a specific device to drive the action of the actuator.
(4) Programmer
The programmer is an important external device of the PLC. The programmer can be used to send the user program to the user program memory of the PLC and to debug the execution of the program and monitor program. The programmer can be structurally divided into the following three types.
(1) Easy programmer
(2) graphics programmer
(3) Universal Computer Programmer
(5) Power supply
The function of the power supply unit is to convert the external power supply (220V AC power supply) into internal operating voltage. Externally connected power supply, through a dedicated switch-mode regulated power supply inside the PLC, converts the AC/DC power supply into the required working power (DC 5V, ±12V, 24V) of the PLC internal circuit, and is an external input device ( Such as proximity switches provide 24V DC power (only for input terminals). The power to drive the PLC load is provided by the user.
(6) Peripheral Interface
Peripheral interface circuits are used to connect handheld programmers or other graphics programmers, text displays, and to form PLC control networks through peripheral interfaces. PLC uses PC/PPI cable or MPI card to connect with computer through RS-485 interface, which can realize programming, monitoring, networking and other functions.
2. PLC software composition
PLC software consists of system programs and user programs.
The system program is designed and programmed by the PLC manufacturer and stored in the system memory of the PLC. The user cannot read, write or change it directly. System programs generally include system diagnostic programs, input processing programs, compiler programs, information transfer programs, and monitoring programs.
The user program of PLC is the program that the user uses PLC programming language, according to the control requirements. In the application of PLC, the most important thing is to use PLC programming language to write the user program to achieve the purpose of control. Since PLC is a device specially developed for industrial control, its main users are the majority of electrical technicians. In order to meet their traditional habits and ability to master, PLC's main programming language uses a computer language that is relatively simple, easy to understand, and image-specific. Language.
1. Graphical instruction structure
2. Clear variable constants
3. Simplified program structure
4. Simplify the application software generation process
5. Enhanced debugging methods
Third, the basic working principle of PLC
The working mode of PLC scanning is mainly divided into three phases, namely the input sampling phase, the user program execution phase, and the output refresh phase. as the picture shows.
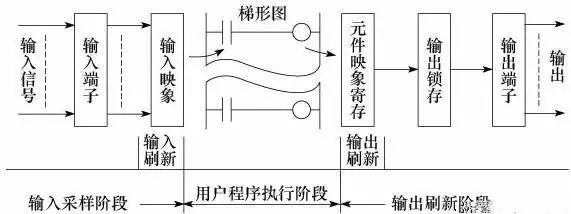
Input sampling phase
In the input sampling phase, the PLC sequentially reads all input states and data in scan mode and stores them in the corresponding cells in the I/O image area. After the input sampling ends, it goes to the user program execution and output refresh phase. During these two phases, the status and data of the corresponding cell in the I/O image area do not change even if the input status and data change. Therefore, if the input is a pulse signal, the width of the pulse signal must be greater than one scan period to ensure that the input can be read in any case. Http://
2. User program execution phase
In the user program execution phase, the PLC always scans the user program (ladder) in order from top to bottom. When scanning each ladder diagram, it is always to scan the control circuit formed by each contact on the left side of the ladder diagram, and perform logical operations on the control circuit formed by the contacts in the order of left, right, first, upper, and lower; Then according to the result of the logic operation, the state of the corresponding bit in the system RAM memory area of ​​the logic coil is refreshed, or the state of the corresponding bit in the I/O image area is refreshed, or it is determined whether to execute the ladder diagram Special function instructions. That is, during the execution of the user program, only the state and data of the input point in the I/O image area will not change, while the status of other output points and software devices in the I/O image area or system RAM memory area will not change. Both the data and the data may be changed, and the ladder diagram above is displayed. The result of the program execution will act on the ladder diagram below which all these coils or data are used. On the contrary, the ladder diagram below is The status or data of the refreshed logic coil can only go to the next scan cycle to work on the ladder diagram that is placed on it.
3. Output refresh phase
After the user program scans, the PLC enters the output refresh phase. During this period, the CPU refreshes all of the output latch circuits according to the corresponding status and data in the I/O map area, and drives the corresponding peripherals through the output circuit. At this time, it is the true output of the PLC.
Input/output hysteresis
From the PLC work process, the following conclusions can be summarized.
Execution of the program in a scanning manner has a principle lag in the logical relationship between the input/output signals. The longer the scan cycle, the more severe the hysteresis.
The scanning cycle includes the time occupied by the system management operations, in addition to the three major work phases of the input sampling phase, the user program execution phase, and the output refresh phase. Among them, the execution time of the program is related to the length of the program and the complexity of the operation of the instruction. The others are basically unchanged. The scan cycle is generally nanoseconds.
· When the nth scan executes the program, the input data is based on the scan value in the sampling phase of the scan cycle X. The output data according to the previous scan has the output value Y(n-1), and the current output value. Yn; The signal sent to the output terminal by n is the final result Yn after all operations are performed this time.
• The input/output response lag is not only related to the scanning method, but also related to the program design arrangement.
Shenzhen MovingComm Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.movingcommiot.com