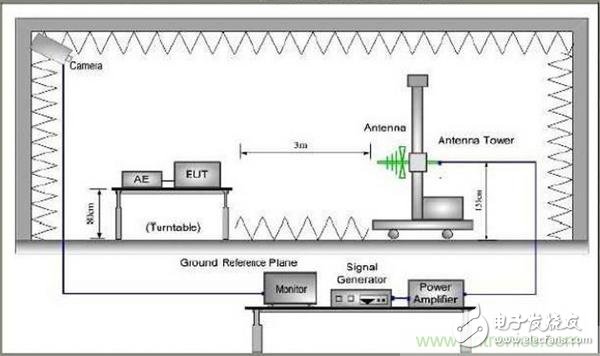
First, a brief description of the basic situation of the radiation test is carried out. The test product is placed on a 0.8 m high-insulation table above the turntable inside a shielded darkroom. The table can be rotated 360°. In addition, at the other end of the product to be tested, at 3m or 10m, there is an antenna tower that can move freely up and down at a height of 1m~4m and can freely switch the polarity of the antenna in both horizontal and vertical directions, and receive the normal operation of the product on the opposite turntable. The field strength generated in the form of electromagnetic waves transmitted through the space is then connected to an external receiver for measurement. The details are as shown below:
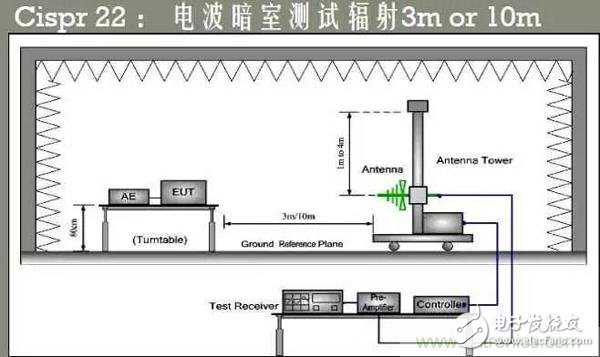
According to the above, the antenna is to receive electromagnetic waves emitted by the product under test in two directions perpendicular to the horizontal direction. The concept and principle of vertical polarization and horizontal polarization of the antenna are first explained as follows:
(1) What is the wave?
In mathematics, any function shape that moves in a certain direction can be considered as a wave, which is simply the propagation of vibration. Each wave has a corresponding quantum, electromagnetic wave - photon, gravitational wave - gravity. Some waves require media such as mechanical waves such as sound waves. Some do not require a medium and can propagate in a vacuum, such as electromagnetic waves. Except for electromagnetic waves and gravitational waves that can propagate in a vacuum, most waves, such as mechanical waves, can only propagate through the medium.
When the wave is transmitted in a uniform, non-directional medium, it can be divided into two forms according to the vibration direction of the medium:
Longitudinal wave: The longitudinal wave is characterized by the same vibration direction of the medium and the propagation direction. In the longitudinal wave, the wavelength refers to the distance between two adjacent dense parts or sparse parts. For example, sound waves in the air and P waves in the seismic waves.
Transverse wave: The characteristic of the transverse wave is that the vibration direction of the medium is perpendicular to the direction of propagation. The transverse wave is also called “convex waveâ€, such as electromagnetic waves, light waves, and S waves in seismic waves. The characteristic of the transverse wave is that the vibration direction of the particle is perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave. The portion protruding in the transverse wave is a peak, and the concave portion is called a trough. Its wavelength usually refers to the distance between two adjacent peaks or troughs.
(2), wave polarization (polarization)
It is stipulated that the direction of the electric field is the polarization direction of the antenna. Generally, the antenna used is single-polarized, and the horizontal polarization and the vertical polarization are two basic single polarizations. Electromagnetic waves are different from longitudinal waves as common acoustic waves. Electromagnetic waves are three-dimensional transverse waves, which are due to their vector characteristics.
The asymmetry of the direction of vibration with respect to the direction of propagation is called polarization (polarization), where the polarization value is greatest when the direction of vibration is perpendicular to the direction of propagation. It is one of the most obvious signs that the transverse wave is different from other longitudinal waves. Only the transverse wave has polarization (polarization). Light waves are electromagnetic waves. Therefore, the direction of propagation of light waves is the direction of propagation of electromagnetic waves. The electric vibration vector E and the magnetic vibration vector H in the light wave are both perpendicular to the propagation velocity v, so the light wave is a transverse wave, which has polarization. Light having polarization is referred to as polarized light. Polarized light is a special electromagnetic wave. Its electromagnetic oscillation only occurs in one direction. The vibration in other directions is 0. There are various kinds of polarized light, such as circular polarized light and elliptically polarized light.
All electromagnetic plane waves are generally divided into straight lines, arcs and elliptically polarized waves.
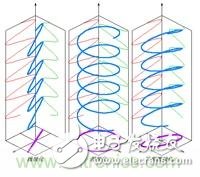
(3) Polarization of the antenna (polarization)
The antenna radiates electromagnetic waves to the surrounding space. Electromagnetic waves are composed of an electric field and a magnetic field. It is stipulated that the direction of the electric field is the direction of polarization of the antenna. Generally used antennas are unipolar. The figure below shows two basic single-polarization cases: vertical polarization - the most common one; horizontal polarization - is also used.
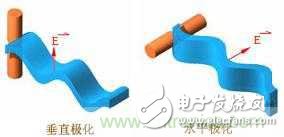
Polarization loss: Vertically polarized waves are received by antennas with vertical polarization characteristics, and horizontally polarized waves are received by antennas with horizontal polarization characteristics. The right-hand circularly polarized wave is received by an antenna having a right-handed circular polarization characteristic, and the left-handed circularly polarized wave is received by an antenna having a left-handed circular polarization characteristic. When the polarization direction of the incoming wave is inconsistent with the polarization direction of the receiving antenna, the received signal will become smaller, that is, polarization loss occurs. For example, when a vertically polarized or horizontally polarized wave is received with a +45° polarized antenna, or when a +45° polarized or -45° polarized wave is received with a vertically polarized antenna, etc. To create polarization loss. Receiving any linearly polarized wave with a circularly polarized antenna, or receiving any circularly polarized wave with a linearly polarized antenna, etc., polarization loss is also inevitable - only half of the energy of the incoming wave can be received.
Polarization is completely isolated: when the polarization direction of the receiving antenna is completely orthogonal to the polarization direction of the incoming wave, for example, a horizontally polarized receiving antenna receives a vertically polarized incoming wave, or a right-handed circularly polarized receiving antenna When receiving a left-handed circularly polarized incoming wave, the antenna will not receive the incoming wave energy completely. In this case, the polarization loss is maximum, and the polarization is completely isolated. The ideal polarization is completely isolated. The signal fed into a polarized antenna will always appear a little bit in another polarized antenna. For example, in the dual-polarized antenna shown in the figure below, the power of the input vertically polarized antenna is 10 W, and the output power measured at the output of the horizontally polarized antenna is 10 mW.
Small computer system interface (SCSI) is an independent processor standard for system level interfaces between computers and intelligent devices (hard disks, floppy drives, optical drives, printers, scanners, etc.). SCSI is an intelligent universal interface standard.
SCSI-3
In 1995, the more high-speed SCSI-3, called ultrasci, was born, and the data transmission rate reached 20MB / s. It increases the synchronous transmission clock frequency to 20MB / s and improves the data transmission rate. If 16 bit wide mode is used, the data transmission rate can be increased to 40MB / s. This version of SCSI uses a 68 pin interface, which is mainly used on hard disks. The typical characteristic of SCSI-3 is that the bus frequency is greatly increased and the signal interference is reduced to enhance its stability.
There are many models of SCSI-3. Ultra (FAST-20) has a transmission frequency of 20MHz, a data bandwidth of 8 bits and a transmission rate of 20MBps
Ultra wide has a transmission frequency of 20MHz, a data bandwidth of 16 bits and a transmission rate of 40mbps
The transmission frequency of ultra 2 is 80 MHz, the data bandwidth is 16 bits, and the transmission rate is 80 Mbps
The transmission frequency of ultra 160 is 80 MHz, the data bandwidth is 16 bits, and the transmission rate is 160 Mbps
The transmission frequency of ultra 320 is 80MHz, the data bandwidth is 16 bits, and the transmission rate is 320mbps
The transmission frequency of ultra 640 is 160MHz, the data bandwidth is 16 bits, and the transmission rate is 640mbps
Plastic SCSI Cover
ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.antenkconn.com