EPS is the abbreviation of English Electric Power Steering, namely electric power steering system. The electric power steering system is the development direction of the automobile steering system. The system directly provides the steering assist by the electric power assisting machine, eliminating the power steering oil pump, hose, hydraulic oil, conveyor belt and the pulley mounted on the engine necessary for the hydraulic power steering system. It saves energy and protects the environment. In addition, it has the characteristics of simple adjustment, flexible assembly and steering assistance under various conditions. It is with these advantages that the electric power steering system, as a new steering technology, will challenge the hydraulic steering system that has been well known and has a history of more than 50 years.
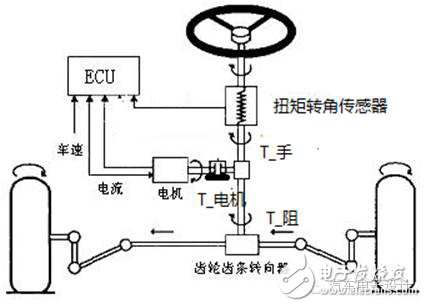
When the driver performs steering on the steering wheel, the torque sensor detects the steering of the steering wheel and the magnitude of the torque, and transmits the voltage signal to the electronic control unit. The electronic control unit detects the torque voltage signal and the direction of rotation according to the torque sensor. And the vehicle speed signal, etc., an instruction is given to the motor controller to cause the electric motor to output a steering assist torque of a corresponding magnitude and direction, thereby generating auxiliary power. When the car is not turning, the electronic control unit does not issue an instruction to the motor controller, and the motor does not work.
The first part of the EPS control strategy
Control strategy is nothing more than three things:
What is the input?
For the EPS control strategy, the input of its basic functions is mainly the steering wheel torque provided by the EPS system internal torque angle sensor, the steering wheel angle, and the vehicle speed signal obtained from the bus.
For some EPS advanced functions, it may be necessary to obtain the vehicle dynamic parameters such as the side angle, the yaw rate, and the left and right front and rear wheel speeds from the CAN bus.
For driving assistance or automatic driving, signals such as superimposed torque values, target steering wheel angles, and target steering wheel speeds are also required to be obtained from the CAN bus.
What is the output?
Based on the input, what kind of control logic is used to get the output?
Due to space limitations, here only the control strategy of EPS basic functions is involved. Please keep in mind the following simplified formula: T_hand+T_motor=T_resistance
The T_ hand is the torque used by the driver to manipulate the steering wheel and is measured by the torque angle sensor.
T_resistance is the torque generated by the friction between the tire and the ground and transmitted to the rack. The process of steering the system is the process of customer resistance.
The EPS control strategy is actually the process of calculating the T_ motor based on various system input conditions. As for how the T_ motor is generated (in the field of motor control)
A careful audience may have to ask, but also use the speed as an input? Where is the speed of the car? Where is the speed?
There are some calibration parameters called CURVE or MAP in all the frames of the technology. The parameters that are annoying are basically related to the speed of the car.
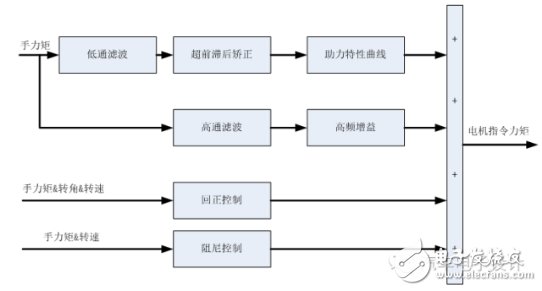
Figure 1: Basic EPS Control Module
Pond Submersible Lightings,Submerge Water Lamp,Multi Water Proof Lamp,Low Voltage Power Supply Lamp
Sensen Group Co., Ltd.  , https://www.sunsunglobal.com