0 Preface
After rapid development in recent years, Embedded System has become one of the most growing branches of the electronic information industry. With the large number of new applications such as mobile phones, PDAs, GPS, set-top boxes, etc., the market for embedded systems is increasing at an annual rate of 30% (IDC forecast), and the design of embedded systems has become a topic of increasing concern for hardware and software engineers. .
In embedded system design, Low Power Design is a problem that many designers must face. The reason is that embedded systems are widely used in portable and mobile products that do not always have sufficient power supply, often powered by batteries; and most embedded devices have volume and Quality constraints. In addition, the heat generated by the system components is proportional to the power consumption, and the cooling measures taken to solve the heat dissipation problem further increase the power consumption of the system. In order to get the best results, reducing the power consumption of the system has the following advantages:
(1) Battery driven needs. While emphasizing green environmental protection, many electronic products are powered by batteries. For battery-powered systems, extending battery life, reducing the cycle of users replacing batteries, improving system performance and reducing system overhead, and even protecting the environment.
(2) The need for security. In the field of fieldbus, the intrinsic safety issue is an important topic. For example, the intrinsically safe equipment of FF can theoretically accommodate 32 devices per network segment, and the practical application considers the current power consumption level, and it is more suitable to install 10 for each network segment. Therefore, reducing system power consumption is an important way to achieve intrinsic safety requirements.
(3) Solve electromagnetic interference. The lower the system power consumption, the smaller the electromagnetic radiation energy and the less interference to other devices. Electromagnetic compatibility design can be easy if all electronics can be designed for low power consumption.
(4) The need for energy conservation. Especially for battery-powered systems, the power consumption is proportional to the square of the voltage: P = V2 / fC + PstaTIc, so energy saving is more important.
1 Reasons for power consumption
1.1 Power consumption of integrated circuits
The current integrated circuit process mainly has two major categories of TTL and CMOS, no matter which process. As long as there is current flowing through the circuit. Power consumption is generated. Generally, there are four main power consumptions of integrated circuits:
(1) Switching power consumption. Formed by charging and discharging a capacitor in a circuit, the expression is:
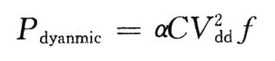
Where: Vdd is the power supply voltage; C is the charged and discharged capacitor: α is the activity factor; f is the switching frequency.
(2) Static power consumption and dynamic power consumption. When the state of the circuit is not flipped (maintained high or low), the power consumption of the circuit is static power, which is equal to the product of the circuit voltage and the current flowing through; the dynamic power consumption is the work generated when the circuit is flipped. Consumption, due to the existence of a transition edge when the circuit is flipped, the current is relatively large at the moment of circuit flipping. There is a large dynamic power consumption. Most of the current circuits use CMOS technology, and the static power consumption is small and can be ignored. The main role is dynamic power consumption, so reduce power consumption by reducing dynamic power consumption.
(3) Short circuit power consumption. Due to the path formed by the power supply to ground during switching, the expression is:
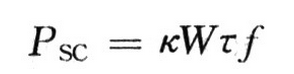
Where: κ is determined by process and voltage; W is the transistor width; τ is the time when the input signal rises/falls; f is the operating frequency.
(4) Leakage power consumption. Caused by subthreshold current and reverse bias current. Most circuits today use CMOS technology. Therefore, the leakage power consumption is small and can be ignored.
1.2 Power consumption of the resistor and power consumption of the active device
Power consumption typically generated for load devices and parasitic components. When the active switching device is in state transition, the current and voltage are relatively large, which will cause power consumption. In addition, the largest power consumption in CMOS circuits comes from the power dissipation caused by internal and external capacitor charging and discharging.
Wall-Mounted Digital Signage,Wall-Mounted Screen,Hanging Display,Digital Lcd Display
Shenzhen Risingstar Outdoor High Light LCD Co., Ltd , https://www.risingstarlcd.com