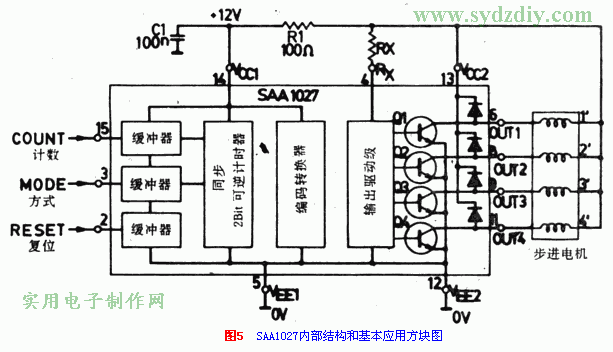
Four-phase stepper motors can use several special integrated circuit drivers. SAAl027 is one of the commonly used ones. It is characterized by a wide operating voltage range of 9.5V to 18V; a large output drive current, up to 500mA. It is suitable for the control of four-phase full-step stepping motor. Figure 4 is the appearance and pin function diagram of SAAl027. Figure 5 (below ↓) is its internal principle block diagram and basic application.
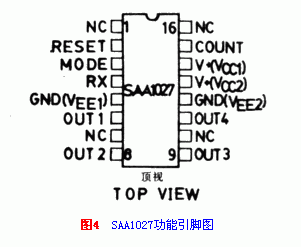
In fact, the integrated circuit has three buffered inputs, and each buffered input controls a two-bit (four-state) synchronous reversible counter. Its output is sent to a transcoder. Then use four outputs to control the four transistors of the output stage. The output stage works with an open collector. The winding coil of the motor is connected into the collector. In order to prevent the reverse electromotive force from damaging the transistor, a reverse diode is connected in parallel at both ends of the winding.
Special attention should be paid to: pins 13 and 12 of the integrated circuit are pins through which a large current flows. And 14 feet and 5 feet flow small current. When in use, pins 5 and 12 must be grounded. Usually plus 12V is directly connected to pin 13, and then to pin 14 via R1-C1 decoupling circuit. Positive voltage must also be sent to pin 4 via Rx. The role of Rx is to determine the maximum output drive current capacity of the four transistors. The size of Rx can be calculated by the following formula;
Rx ï¼ (4E ï¼ I) ï¼6
Where E is the power supply voltage and I is the desired maximum phase current of the motor. When using 12V, Rx value takes 420Ω, 180Ω or 78Ω), the maximum output current is 100mA, 200mA, or 350mA respectively.
SAA1027 integrated circuit has three input control terminals: counting, mode and reset. The reset terminal is usually high. Every time the counter changes from low to high, the integrated circuit will change state. All working conditions have been listed in Table 3.
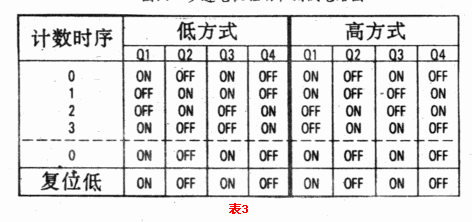
At any time, the sequence repeats every four steps. However, when the reset terminal is low, it can be reset to the initial state.
When the mode control input is low, the sequence repeats in one direction (usually clockwise rotation). Conversely, when the mode control terminal is at a high level, the sequence is repeated in the other direction (counterclockwise rotation).
Figure 6 is the drive and test circuit of SAAl027.
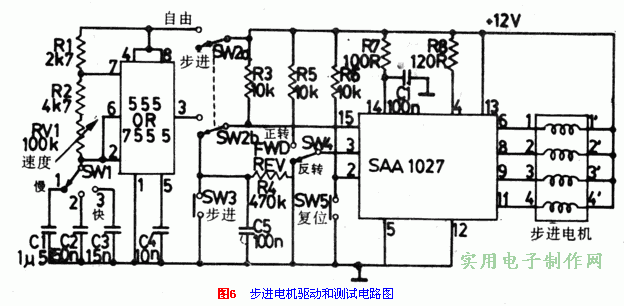
This circuit is used in a hybrid four-phase stepper motor with a rated current up to 300mA. The motor can be used for manual single-step test with SW3, or for automatic stepping test with SW2 via 555/7555 unstable oscillator. SW4 can control the direction of the motor. SW5 is used for reset control test.
With the SW1 and RV1 potentiometers, the working speed of the unstable circuit can be changed within a wide range. When set to 1st gear, it is low speed control, and the frequency range is from 5Hz to 68Hz. When SW2 is in 2nd and 3rd gears, the oscillation frequency is 10 times and 100 times of the 1st gear respectively. The total speed control range is from 6-8500 rpm.
Figure 6 is a basic circuit. According to different occasions, there are several changes.
Figure 7 is an interface circuit between a stepper motor and a microprocessor.
The output port of a computer or microprocessor is usually regarded as a logic 0 state when the terminal drive voltage is lower than 1V; and as a logic 1 state when it is higher than 3.5V. This logic is called positive logic. However, the circuit in Figure 7 is the opposite of the above. Therefore, when the input end of the stepping motor changes from high level to low level, the working state changes. The reset terminal is reset with a high level. When the mode input is low level, the motor rotates forward; when the level is high, the motor reverses.
The maximum output current of the circuit design in Figure 6 is 300mA.
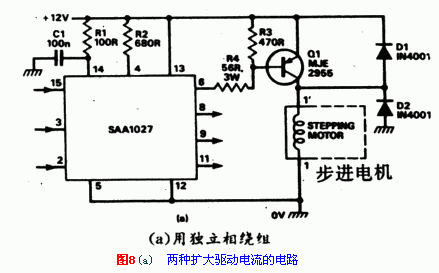
If you want to extend the current by 5A, use the two circuits in Figure 8. Each phase of the stepper motor requires an additional drive circuit, and a four-phase stepper motor needs to add four such additional circuits. The circuit in Fig. 8 (a) is used for the driving circuit. A four-phase stepper motor needs to add four such additional circuits. The circuit of Figure 8 (a) is used to drive four completely independent windings. The circuit of Fig. 8 (b) is used for stepping motors whose windings have a common point. The role of D1 and D2 is to prevent the back-EMF of the motor from damaging the output stage transistors.
Coin/Button Cell-retainers And Contacts
Antenk coin cell battery retainers Designed for memory back-up and stand-by applications, these contacts permit quick and easy coin cell replacement and installation. Eliminating "soldered-in" cells, computer, video, telecommunication and similar PCB based product users now have a reliable, "no tools required" method for changing batteries.
Extremely economical, these retainer contacts are available in surface mount (SMT) or thru hole mount (THM) styles for 4.8mm, 6.8mm, 11.6mm,12mm, 16mm, 20mm, 23mm and 24mm coin cells. The THM version has stable mounting legs for excellent board retention during wave solder. The SMT version includes a unique solder tail "flow-hole" design to bolster reflow and strengthen solder joints. They are manufactured from phosphor bronze, precision stamped and are plated with either a high luster nickel finish or matte tin finish ideal for low temperature soldering enviornments. Both feature dual spring contacts to assure reliable connections and a low contact resistance.
Antenk Coin/Button Cell-retainers And Contacts

Coin cell retainers are simple metal contacts that both electrically connect coin cells and hold them in place, while taking up minimal additional space on the PCB. They feature nickel-plating, and since most coin cells have nickel shells this helps to prevent galvanic corrosion, an electrochemical process that can damage dissimilar metals that are in electrical contact. Our retainers are always designed with automation in mind, and can be easily picked and placed, with both through hole and surface mount retainers available for most coin cell sizes. Combining the ease of automation with the low cost of Antenk's retainers, it is no wonder they are such a popular product.
Coin Cell, Button Cell, Retainers, Contacts
Designed for memory backup and standby applications, Antenk's compact coin cell battery retainers permit quick and easy coin cell replacement and installation. By eliminating soldered-in cells, computer, video, telecommunication, and similar PCB based product users now have a reliable, no tools required method for changing batteries.
These holders and retainers are available in surface-mount (SMT) or through-hole-mount (THM) styles for 4.8 mm to 24 mm coin cells. The THM version has stable mounting legs for excellent board retention during wave soldering. The SMT version includes a unique solder tail flow-holedesign to bolster reflow and strengthen solder joints. Both feature dual spring contacts to assure reliable connections and low contact resistance.
Coin Cell, Button Cell, Retainers, Contacts Features
Available in THM or SMT configurations
SMT solder tail with flow-hole design for increased joint strength
SMT solder tail located outside of retainer body which facilitates visual inspection of the solder joints
THM legs maintain relative position during and after soldering
Reliable spring tension assures low contact resistance
Retains battery securely to withstand shock and vibration
Ideally suited for high-density packaging
Ideal for low-profile space-saving PCB applications
Designed for reflow and all PCB soldering applications
Compatible with all wave and reflow operations
Compatible with most vacuum and mechanical, pick and place assembly systems
Matte-tin plate for lower soldering temperatures ideal where other temperature sensitive components are being used
Tin-nickel plated retainers are ideal for lead-free, high-temperature soldering applications
Retainers available for coin cell batteries from 4.8 mm to 24 mm diameter
Coin Cell Retainers by Size of Cell
191 | 335 | CR1025 | CR1216 | CR1220 | CR1225 | CR1632 | CR2016 | CR2032 | CR2320 | CR2325 | CR2330 | CR2354 | CR2430 | CR2450 | CR2477 | F3 iButton | F5 iButton | LR1120 | LR44 | ML414 | SR512SW | SR60 | V80H or CP1654 | BR1025 | BR1216 | BR1220 | BR1225 | BR1632 | BR2016 | BR2032 | BR2320 | BR2325 | BR2330 | BR2450 | BR2477 | Other Sizes
Button Contacts,Coin Cell Retainers And Contacts,Coin Cell Retainers
ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.pcbsocket.com