Murray Slovick
With the introduction of electronic medical records (EHR), mobile medical devices and medical cloud computing, the medical industry is facing new security challenges. According to the McAfee Report 2013 Threat Prediction, the threat of mobile medical devices rose significantly in the middle of last year. Similarly, what is Intel reporting on the trail of the cloud? It was found that 65% of respondents believe that using cloud infrastructure is more violating than traditional IT infrastructure. Managing these risks is a challenge. Mobile devices can easily fall into the wrong hands, and cloud solutions often have limited security controls. As more types of devices connect to each other, authentication becomes more and more complex.
There is no doubt that any level of security will not solve all these risks. On the contrary, smart medical security requires a series of defenses in the system through a layered platform approach so that if one layer of security is compromised, the other layer is readily available. To meet this goal, security must be an integral part of the design process from the beginning, so that security features are included in every key layer of the hardware and software stack. Entering the Intel® Intelligent Systems Framework, the broad technical specifications of embedded systems bring together hardware, operating systems (OS) and tools for the development of secure interconnect devices. In this article, we will describe how the framework builds on the fundamental advantages of Intel® architecture processors such as the 3rd generation Intel® CoreTM processor to enable multi-layered protection of medical systems.
safe question
We first delve into the complex nature of medical device safety: What are the customer issues and what are the overall prospects? Because of the simple reason that information has enormous value, medical systems are increasingly attacked. Medical records are particularly vulnerable to safety leaks because their shelf life is much longer than credit card numbers. In addition, credit cards can be revoked while medical records cannot. Therefore, the medical field has become the main goal of hackers who are aiming to steal information for profit. According to the World Privacy Foundation, stealing of medical identity in the United States alone affects 1.5 million people and brings more than $30 billion in costs. The uniqueness of medical records is also highly personal, which makes confidentiality a necessary legal requirement. In the United States, for example, medical devices must comply with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) rules for the storage of patient data.
Multi-layered defense
To help protect medical data, Intel, Wind River and McAfee have developed a medical security reference platform. This concept demonstrates the convergence of security technologies such as hardware encryption, virtualization, operating systems, and service software (see Figure 1). The platform is designed using existing components and applies security policies that comply with standard IT practices.
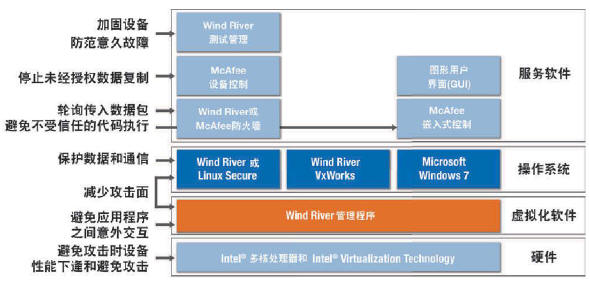
Figure 1. The medical security reference platform implements multi-layered security.
In addition, the full software stack complies with the Intel Intelligent Systems Framework. The framework defines a set of functions required to achieve connectivity, security, and manageability between devices in a consistent and scalable manner. The framework simplifies hardware and software integration and releases time for focusing on intelligent data sharing and analysis, commonly referred to as "big data." Because the medical security reference platform is built around the framework, software can be quickly deployed on hardware platforms that support the framework. This feature allows the use of solutions on multiple medical devices.
The Medical Security Reference Platform also demonstrates the value of the Intel® Intelligent Systems Alliance, and Wind River and McAfee are partners. From modular components to market-enabled medical systems, Intel and the 250+ Intel Intelligent Systems Alliance global partner companies provide the performance, connectivity, manageability, and security developers need to create smart, connected systems. Alliance members work closely with Intel and each other to ensure that they use the latest technology to innovate and help developers provide the market's earliest medical solutions to improve patient care and electronic record retention.
Now let's learn more about the main security layer.
encryption
Portable devices allow higher mobility between medical practitioners, but if the device is lost or stolen it will increase the risk of safety leakage. Data encryption mitigates this risk and simplifies management. Encrypted devices are “safe havens†under the HIPAA security regulations—that is, if the encrypted device is lost or stolen, there is no need to notify the patient of the leak. Similarly, cloud computing requires the ability to encrypt still and transmit data. Unencrypted data transmission is easily manipulated. For example, malware can access and modify data and affect patient safety. In general, encryption ensures that attackers do not have access to usable data and the attacked device continues to work properly.
The 3rd generation Intel Core processor supports data encryption through the Intel® Advanced Encryption Standard New Instructions (Intel® AES-NI). This hardware-assisted security technology significantly accelerates the AES algorithm, allowing encryption of still and mobile data, with minimal impact on device performance. For example, the BitLocker Drive Encryption feature in Microsoft Windows 7 uses Intel AES-NI encrypted files and even the entire driver, with minimal performance impact.
Virtualization
Multi-core Intel Core processors are increasingly used to combine common OS (GPOS) such as Linux or Microsoft Windows on the same platform with real-time OS (RTOS) such as Wind River VxWorks. Typically GPOS is used for non-critical functions, such as human/machine cross-sections, while safety-critical applications run on RTOS.
Separation of secure and non-secure applications is achieved through a hypervisor (sometimes called virtual machine monitor) software layer between the hardware and the operating system. The hypervisor provides each guest operating system with a "virtual machine" (VM) that looks like a dedicated hardware platform (Figure 2). The hypervisor manages the guest operating system and ensures that the software running in the VM can only access its own resources, such as the memory dedicated to that VM, to exclude unauthorized access.
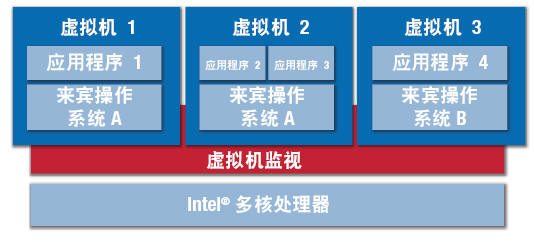
Figure 2. Virtualization enables secure separation of secure and non-secure applications.
For medical applications, this feature allows relatively unimpeded operation of safety-critical applications, even if the virus runs on other VMs, or at least until dangerous conditions are identified and corrective action can be taken. This secure partition makes the device less vulnerable to external threats and tampering. For example, a network connection can be hosted in its own VM so that it can isolate any attacks on that connection without seriously affecting device capabilities.
The hypervisor can also be used to implement a virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) that instantiates multiple desktop operating systems on a central server. In this model, applications and data remain on the server for customers to access using remote display protocols. VDI minimizes the risk of data loss from stolen or lost devices because no application is running locally on the device and no data is stored on the device.
Wind River Hypervisor supports these and other virtualization simulations by partitioning a platform into a hypervisor with multiple layers of protection and functionality. This is a Type 1 hypervisor that runs directly on the hardware and uses a small amount of memory. Wind River Hypervisor is also designed from the ground up to achieve scalability, ensuring that performance does not suffer when the number of cores increases.
Partitions are more efficient when deployed on the 3rd generation Intel Core processor family. These processors support Intel® Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT), a set of hardware virtual accelerators that improve security, management, and control while improving application performance and responsiveness. Intel VT protects the memory space in the hardware and helps prevent malware attacks.
Overall, Intel's multi-core and virtualization technologies can dramatically improve the performance and reliability of medical devices and reduce time-to-market. With these technologies, medical device OEMs can incorporate more features into the final system, reduce costs and complexity, and meet challenging safety and regulatory certification requirements.
whitelist
After the device is connected to the network, it is vulnerable to malware attacks - through tampering or accidental installation - putting the patient's property at risk. Malware also brings support issues and violates software licenses and threatens the entire system. To deal with these possibilities, security needs to be implemented to prevent unauthorized software from executing.
There are two main ways to ensure that medical devices can only execute trusted applications: blacklists and whitelists. The blacklist uses antivirus software to search for known bad software on the "blacklist" and eliminate threats. The whitelist evaluates requests for running programs or scripts. The security software checks here whether the program or script is on the "white list" of software that is approved for operation. If the answer is yes, the program is allowed to execute. If the answer is negative, an illegal execution attempt is recorded and/or reported, allowing the system administrator to take preventive measures as needed.
For example, McAfee's application whitelisting solution prevents malware from threatening and infecting embedded devices. Its embedded control for healthcare allows only authorized code to run and authorize changes to the system, especially maintaining integrity. Embedded control automatically creates a dynamic whitelist of authorization codes on the embedded system. After the white list is created and enabled, the system is locked and any program or code outside the authorization set cannot be run and unauthorized changes cannot be made.
McAfee Embedded Control specifically addresses many of the requirements of HIPAA and FDA by controlling the software's operational and modifiable content on any system. It ensures that any software changes happen only through authorization mechanisms—for example, authorizing change control windows, authorizing updates, or security signature updates. It also provides the ability to capture authorization change audit records, which in turn helps compliance and reporting to meet HIPAA's data security requirements for factors and auditable controls.
These software features are complemented by two hardware features in the 3rd generation Intel Core processor. Intel® Trusted Execution Technology (Intel® TXT) provides measurement initiation of hypervisors and operating systems to ensure that the system boots up into a trusted state. While Intel® Active Management Technology (Intel® AMT) provides an out-of-band communication channel to enhance security, IT management can reach the device through this channel even if the device is turned off or the operating system (OS) is not working or is missing. If the device is threatened by malware or fails, administrators can quickly diagnose and repair problems and go straight to the firmware layer. With Intel AMT, supporting organizations can also isolate the compromised devices from the rest of the network and prevent the spread of malware.
Protect data and communications
After being threatened, medical equipment can become a base for hackers to launch attacks on other devices and systems on the hospital's network. To avoid this situation, it is best to use an operating system such as Wind River Linux Secure, VxWorks, or Microsoft 7 to defend against the computing environment. These operating system certifications have reached Common Criteria Evaluation Assurance 4+ (EAL4+). The evaluation rating of IT products is a numerical rating assigned after the completion of the public standard security assessment. This is an internationally recognized standard (ISO 15408) for measuring IT product safety. EAL 4+ is the highest level of certification recognized by both parties and requires the most in-depth evaluation level of an independent testing laboratory.
Viruses usually access medical devices via the network, and they can be hidden in spurious packets on the network. Adding a McAfee or Wind River firewall to a device ensures that it will query incoming packets, avoid untrusted code execution, and in this way protect the protocol stack from security leaks. The firewall also discards unwanted packets and records packets that can be used to identify potentially malicious operations later.
Similarly, McAfee Device Control protects data from falling into the wrong hands via removable storage devices and media such as USB flash drives or Bluetooth peripherals. It allows device designers to specify and classify devices that can be used or not, specifying the data that can be transmitted and non-transmitted by these devices (see Figure 3).
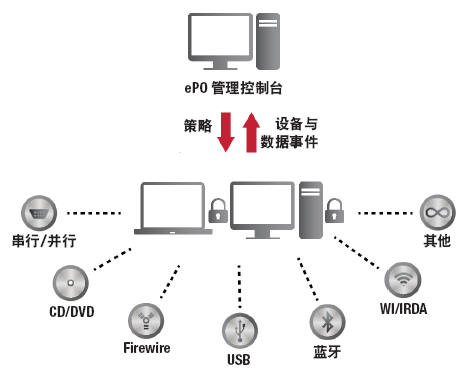
Figure 3. McAfee Device Control specifies usable devices and reproducible data.
Safety test
Eliminating vulnerabilities is one of the best ways to handle system vulnerabilities. Many security risks are the result of untested code that contains bugs, provides unexpected input, or has other security holes. The key to dealing with this kind of problem is to predict the paths that can be used to attack the device and try to cause it to go wrong under negative conditions. Wind River Test Management helps developers perform this kind of testing, including the following features:
· Code coverage analysis of real-time production code
Automatic performance degradation test
· Binary code change analysis to reduce retesting and marking suspect code
· Simulate attacks with precise fault injection and "violent" fuzz testing
For example, fuzz tests provide invalid or random data to various protocols and input files used by medical devices. The tool automates this test and runs thousands of test cases on the device, speeding up the diagnosis and helping developers efficiently identify potential vulnerabilities before shipping the device. Wind River Test Management brings a clear view of device operations under test so that non-specialist testers can perform safety tests and understand the results.
Must establish safety
As part of the development process, designers need to find ways to avoid invading personal devices and networks or at least mitigate the effects of intrusions. Engineers must understand and accept that addressing security concerns is an integral part of the design process. The designer must understand this fact and cannot retaliate after the development cycle.
The Intel Intelligent Systems Framework is designed to make it easier for embedded design engineers to achieve these goals, providing a safer foundation for building next-generation medical devices and enabling them to get to market faster. Support for new technologies and components from Intel and the Alliance will make it easier to deploy a more secure medical device infrastructure.
Immersion Cooling is a technique used to cool components of IT equipment that consists of submerging the computer components in a thermally conductive and dielectric liquid. Through this practice, the servers are cooled and heat is transferred from the source to the liquid.
When we talk about Immersion Cooling, we also need to discuss the different types of Immersion Cooling, as well as the applications of Immersion cooling. The practice of Immersion Cooling has a multitude of benefits particularly as it allows datacenters to be managed in a greener and more sustainable manner. Environmental concerns has been a huge catalyst for the adoption of the technology in recent years.
deionized water
mineral oil
fluorocarbon-based fluids
synthetic
Immersion Cooling systems used to have a higher fluid cost than water cooling, but this is already changing.
A wide variety of liquids exist for this purpose, the most suitable being transformer oils and other electrical cooling oils. Non-purpose oils, including cooking, motor and silicone oils, have been successfully used for cooling personal computers
water cooling,oil cooling,immersion cooling box,liquid immersion cooling,apw12 power supply
Shenzhen YLHM Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.apgelectrical.com